Spotlight on Massage and Lower Back Pain
 According to the National Institutes of Health, lower back pain is the second most common form of chronic pain after headaches. Experts estimate that approximately 80% of Americans will seek help for low back pain at some point during their lives. Public health officials and insurers estimate that Americans spend $50 billion each year on treatments that are often ineffective. The standard treatment for lower back pain is to take muscle relaxants, painkillers or anti-inflammatory medications, along with physical therapy and back exercises. However, few medical interventions relieve pain reliably, and continuing to take painkillers on a long-term basis is not advised. Massage, on the other hand, has been found to be an effective way of dealing with back pain on a regular basis.
According to the National Institutes of Health, lower back pain is the second most common form of chronic pain after headaches. Experts estimate that approximately 80% of Americans will seek help for low back pain at some point during their lives. Public health officials and insurers estimate that Americans spend $50 billion each year on treatments that are often ineffective. The standard treatment for lower back pain is to take muscle relaxants, painkillers or anti-inflammatory medications, along with physical therapy and back exercises. However, few medical interventions relieve pain reliably, and continuing to take painkillers on a long-term basis is not advised. Massage, on the other hand, has been found to be an effective way of dealing with back pain on a regular basis.
Treatment for lower back pain accounts for approximately a third of all visits to a massage therapist. A study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine found that patients suffering from lower back pain of unknown origin were helped more by massage than by conventional medical treatment. Of 401 total study participants, 133 received traditional medical care with no massage, 132 received structural massage (which addresses particular muscular and skeletal structures that cause pain) and 36 received relaxation massage (a general form of massage, such as Swedish, intended for overall relaxation).
Participants in the massage groups received one hour-long massage once a week for 10 weeks. All participants completed a questionnaire at the beginning of the study, then again at 10 weeks, 24 weeks and a year after the beginning of the study to report on their perceived pain. Both kinds of massage groups reported greater pain relief and ease of motion after 10 weeks of treatment than the medical group.
An average of 37% of the patients in the massage groups reported that their pain was almost or completely gone, while only 4% of the usual care group reported similar results. This was also the case at 26 weeks. However, at the one-year mark, the benefits to all groups were about equal. The type of massage used did not seem to matter, with both massage groups experiencing comparable levels of pain relief. The massage groups were less likely to report having used medication for their back pain after the 10 weeks of intervention, and they also reported having spent fewer days in bed and had lost fewer days of work or school than those in the usual care group.
Dr. Richard A. Deyo, professor of family medicine at Oregon Health and Science University in Portland says of the study, “I think this trial is good news in the sense that it suggests that massage is a useful option that helps some substantial fraction of these patients. Like in most other treatments, this is not a slam dunk, and it’s not like a cure, but it’s something that seems to offer a significant benefit for a substantial number of patients.” Deyo sees massage as a way of people being able to break out of the pain-inactivity cycle. He notes, “I don’t see massage as the final solution, I see it as maybe a helpful step toward getting people more active.”
As always, chiropractic care shows the greatest success in the treatment of all types of back pain. We have found that chiropractic care combined with massage can be a very effective option for many of our patients. If you are currently experiencing back pain, be sure to call our office to schedule an appointment with Dr. Oblander. 406-652-3553

 Most teens experience headaches at some point and many will suffer the debilitating impact of persistent headaches or migraines. Chronic headaches can prevent teens from engaging fully in school, work, and extracurricular activities. Yet little was known about what triggers headaches in teens until now.
Most teens experience headaches at some point and many will suffer the debilitating impact of persistent headaches or migraines. Chronic headaches can prevent teens from engaging fully in school, work, and extracurricular activities. Yet little was known about what triggers headaches in teens until now. Many studies have found that chiropractic care is a safe and effective treatment method when dealing with a number of spine-related issues. The American Chiropractic Association even lists a number of research studies on their website that show that it is a valuable treatment method for easing (and sometimes completely resolving) back pain, neck pain, headaches, and more.
Many studies have found that chiropractic care is a safe and effective treatment method when dealing with a number of spine-related issues. The American Chiropractic Association even lists a number of research studies on their website that show that it is a valuable treatment method for easing (and sometimes completely resolving) back pain, neck pain, headaches, and more. Countless studies have demonstrated that chiropractic care is a safe and effective way to treat musculoskeletal complaints like back pain, neck pain, or sciatica. Now a new study from Switzerland has looked at the relative benefits of chiropractic compared to medical care for the most common types of pain issues.
Countless studies have demonstrated that chiropractic care is a safe and effective way to treat musculoskeletal complaints like back pain, neck pain, or sciatica. Now a new study from Switzerland has looked at the relative benefits of chiropractic compared to medical care for the most common types of pain issues.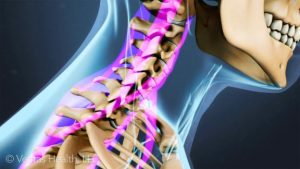 Most people at some point have heard cracking or grinding noises in their neck upon movement. These sounds, also called crepitus, are usually painless and typically do not represent anything serious.
Most people at some point have heard cracking or grinding noises in their neck upon movement. These sounds, also called crepitus, are usually painless and typically do not represent anything serious.
 When it comes to helping elite athletes prevent and recover from injuries—as well as achieve peak performance—chiropractic care can offer many advantages. That’s why large numbers of professional and college sports teams throughout the U.S. have turned to chiropractors over the past decade. The Philadelphia Phillies is one such team, and Dr. Michael Tancredi is one such chiropractor. As a Doctor of Chiropractic, a Certified Chiropractic Sports Physician, an Active Release Technique Instructor and Practitioner, and a certified athletic trainer, Dr. Tancredi clearly understands the valuable role that chiropractic care can play in keeping teams healthy and performing at their best.
When it comes to helping elite athletes prevent and recover from injuries—as well as achieve peak performance—chiropractic care can offer many advantages. That’s why large numbers of professional and college sports teams throughout the U.S. have turned to chiropractors over the past decade. The Philadelphia Phillies is one such team, and Dr. Michael Tancredi is one such chiropractor. As a Doctor of Chiropractic, a Certified Chiropractic Sports Physician, an Active Release Technique Instructor and Practitioner, and a certified athletic trainer, Dr. Tancredi clearly understands the valuable role that chiropractic care can play in keeping teams healthy and performing at their best.
 The Mayo Clinic describes second impact syndrome (SIS) as a complication arising from a concussion. It occurs when someone experiences a second concussion prior to fully recovering from the initial one. With SIS, “typically fatal brain swelling” occurs. R.C. Schneider first described this condition in 1973, but it wasn’t until 1984 that someone gave it the name, “second impact syndrome”. The condition is rare enough that only 21 cases had been cited in the literature up until 2003.
The Mayo Clinic describes second impact syndrome (SIS) as a complication arising from a concussion. It occurs when someone experiences a second concussion prior to fully recovering from the initial one. With SIS, “typically fatal brain swelling” occurs. R.C. Schneider first described this condition in 1973, but it wasn’t until 1984 that someone gave it the name, “second impact syndrome”. The condition is rare enough that only 21 cases had been cited in the literature up until 2003.