The Ultimate Healthy Blueberry Muffin Recipe
[amd-zlrecipe-recipe:1]
Here is a healthy, low-sugar and no refined sugar recipe! You might think about making a batch for Sunday brunch this weekend!
[amd-zlrecipe-recipe:1]
Here is a healthy, low-sugar and no refined sugar recipe! You might think about making a batch for Sunday brunch this weekend!

Today we are sharing an article from Forbes magazine on how losing weight can save you money. Just ask our doc – Dr. Greg Oblander, losing weight saves you more than just money. Think that you are doomed to all of the health woes and diseases that have plagued your parents and grandparents? Would it surprise you to know that genetics only affect about 5% of health issues? Yup, it’s true. Our health is mainly determined by our health and lifestyle choices. Love that Big Mac? Well…it doesn’t love you! Today’s article cites a report that estimates that losing weight will save the average person at least $10,000 over a lifetime. We think that estimate is way low. (Think cost of cancer treatment, heart surgery, escalating medical costs). Money issues aside, how much is it worth to you to not have chronic pain, joint issues, arthritis, heart disease, diabetes, cancer…and the list goes on? Deciding now to get rid of extra weight and adopt the habit of exercise and eating real food will save you both health woes and money! An added bonus is that you will learn a greater degree of self-discipline! If you would like to change your lifestyle habits and/or lose weight, we can help! Call our Oblander Chiropractic office at 406-652-3553 and schedule your free consultation!
Please enjoy today’s article from Forbes magazine:
Losing weight can save you money over your lifetime.
Want another reason to lose weight? How about making your wallet heavier? In our study just published in the journal Obesity, we showed how much money that losing weight can save at any age, whether you are Millennial at 20 years old or a member of the Greatest Generation at 80 years old.
Five members of our Global Obesity Prevention Center (GOPC) at Johns Hopkins University (Saeideh Fallah-Fini, Atif Adam, Lawrence J. Cheskin, Sarah M. Bartsch and I) developed a computational model that simulated an adult at different starting ages and weights and calculated what could happen to the person’s weight, health and associated costs over time for the rest of his or her life. (Dr. Fallah-Fini is also an Assistant Professor of Engineering at the California State Polytechnic University.) Think of this model as a virtual person whom we can follow like a friend while the person ages.
For example, a simulated person could start as overweight at age 20 and then with each passing simulated year of the person’s life gain or lose weight and develop different types of chronic weight-related conditions such as diabetes, heart disease and cancer, just like a real person. The simulation would continue until the person died from either age-related causes or a weight-related condition such as having a fatal heart attack.
At the end of the simulation, we could then tabulate the amount of medical costs that occurred (e.g., hospitalizations and medications for stroke) and the amount of productivity losses that resulted (e.g., lost salary from being disabled or missing days of work for hospitalizations, clinic visits, falling ill or passing away early). By running the model with different starting weights (e.g., within the ideal body weight range) and then comparing the results, we could then see how medical costs and productivity losses may change with losing or gaining weight.
The model utilized data from a variety of sources such as the Coronary Artery Disease Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) and Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) studies, the Framingham Heart Study (FRS), the Northern Manhattan Stroke cohort study, the National Cancer Institute database, the National Health Interview Survey, the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) and the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Dr. Adam played a major role in assembling and analyzing all of this data to help construct the model.
On average, going from obesity to normal weight, a 20-year-old could save a net present value of more than $28,000 throughout their lifetime, a 40-year-old more than $30,000, a 50-year-old more than $36,000, a 60-year-old more than $34,000, a 70-year-old more than $29,000 and an 80-year-old more than $16,000.
Going from overweight to an ideal weight range could save more than $10,000 at any age from 20 to 80, peaking at age 60 ($18,604). It may be that “love don’t cost a thing,” but obesity or being overweight certainly do.
In nearly all situations, at least half of these costs are from productivity losses (lost salary). In many cases, productivity losses constituted as high as nearly two-thirds of the costs. Since we used median wages, if you make much more, then losing weight could save you substantially more than the numbers we reported.
These numbers actually may be underestimates because the model focused on just a handful of major weight-related health conditions. We didn’t account for costs associated with a number of other weight-related issues such as joint problems and mental health issues such as anxiety and depression.
Extra weight not only hits you in the gut, but potentially in the heart, the brain, the liver, the kidneys and other parts of the body, and also the wallet.
And since we are all connected with each other via taxes (assuming that you pay taxes), insurance premiums (assuming that you pay for insurance) and the economy (assuming that you are a person and not a wombat), extra weight for someone else also may end up hitting your wallet, too.
Today’s article is shared from the following website: https://www.forbes.com/sites/brucelee/2017/09/27/how-much-money-you-can-save-from-losing-weight-at-different-ages/#7a2e40295c2a
 Extreme Makeover features a celebrity trainer helping very overweight individuals reach their weight loss goals. Sometimes, their attitudes aren’t great, but other times, the people on the show are truly amazing, like Sara. Sara is a little person, standing at only 4’5″. She was a nutrition speaker on local television shows at the start of her journey, but ashamed of herself. Not only had she spent her life dealing with her short stature, but she had suffered greatly at the hands of her sister. She turned to eating and by the time she was 37 years old, weighed over 200 pounds.
Extreme Makeover features a celebrity trainer helping very overweight individuals reach their weight loss goals. Sometimes, their attitudes aren’t great, but other times, the people on the show are truly amazing, like Sara. Sara is a little person, standing at only 4’5″. She was a nutrition speaker on local television shows at the start of her journey, but ashamed of herself. Not only had she spent her life dealing with her short stature, but she had suffered greatly at the hands of her sister. She turned to eating and by the time she was 37 years old, weighed over 200 pounds.
 When she began her time on Extreme Makeover, her first challenge was to climb the stairs of an amphitheater holding an 80 pound weight. The stairs came up past her knees. But she didn’t complain once. She kept going. Slowly, all the people in the theater started to watch her. By the time she reached the last step, the crowd cheered for her.
When she began her time on Extreme Makeover, her first challenge was to climb the stairs of an amphitheater holding an 80 pound weight. The stairs came up past her knees. But she didn’t complain once. She kept going. Slowly, all the people in the theater started to watch her. By the time she reached the last step, the crowd cheered for her.
Her trainer gave her the goal to run a half marathon 6 months after starting her diet and exercise program. Sara said no. She wouldn’t run the half. Instead she would run a full marathon. Her trainer advised against it because it would be extra hard on her body. She’d have to take many extra strides due to her short stature. Sara didn’t care. She ran the whole marathon.
She succeeded in loosing more than half her body weight and becoming a runner, like she had always dreamed.
If you would like to follow Sara’s example and lose weight and begin your inspirational journey of change, be sure to contact our office to get the details on our ChiroThin diet. It is doctor supervised and is amazing in its ability to not only help you lose weight but also learn new and healthier eating habits! What a win/win! Office phone number: 406-652-3553.
Story is shared from the following website: https://www.livin3.com/5-motivational-and-inspiring-short-stories
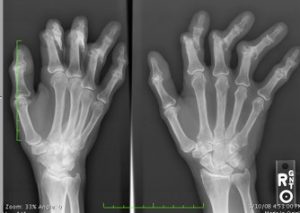 We’ve all heard that calcium is crucial for preventing bone and joint problems, but new research suggests there may be another mineral we need to be mindful of: zinc. In particular, a study suggests that levels of zinc within the cartilage cells may help to explain why tissue destruction occurs in patients with osteoarthritis.
We’ve all heard that calcium is crucial for preventing bone and joint problems, but new research suggests there may be another mineral we need to be mindful of: zinc. In particular, a study suggests that levels of zinc within the cartilage cells may help to explain why tissue destruction occurs in patients with osteoarthritis.
Arthritis is a leading cause of disability in the world, affecting 52.5 million adults in the US alone. Despite the prevalence of osteoarthritis, there are currently no cures to stop the progression of cartilage destruction that takes place in individuals with the condition. Researchers are still attempting to understand what happens at a molecular level to cause the tissue degradation.
Osteoarthritis results in the break down of cartilage between the bones, causing joint stiffness and swelling. Tissue destruction is caused by proteins called matrix-degrading enzymes, which are produced by cells within the cartilage. Matrix-degrading enzymes need zinc to survive, which led researchers to hypothesize that zinc levels play an important role in osteoarthritis.
Using lab mice, the researchers found that a protein called ZIP8 is responsible for transporting zinc within the cells, setting off a chain of events that eventually results in cartilage destruction. Their findings suggest that treatments to deplete zinc in the cartilage cells or inhibit this ZIP8 function may help to stop osteoarthritis. If the research is confirmed in future studies, keeping zinc levels in check could become an integral part of osteoarthritis treatment.
Many patients with osteoarthritis find that it can be successfully managed by a conservative, multimodal treatment, including exercise, nutrition, and chiropractic care. Research suggests that a combination of chiropractic and exercise can significantly ease symptoms in patients with osteoarthritis in the knees, hip, and hands.
Article was written by Marissa Luck and is shared from www.chironexus.net
References
Zinc may be missing link for osteoarthritis therapies. Medical News Today. February 17, 2014. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/releases/272658.php.
Cell, Kim et al. Regulation of the catabolic cascade in osteoarthritis by the zinc axis.
 Anyone with a chronic pain condition like fibromyalgia knows it can be difficult to adhere to a complex set of treatment instructions: physical therapy, medications, creams, journals, the list goes on. We get busy or forget and sometimes don’t comply completely with the treatment, but sooner or later the pain creeps back in. It turns out that regular chiropractic visits can actually help fibromyalgia patients adhere to long-term physical-therapy programs, thereby ensuring that patients receive the full benefits of exercise.
Anyone with a chronic pain condition like fibromyalgia knows it can be difficult to adhere to a complex set of treatment instructions: physical therapy, medications, creams, journals, the list goes on. We get busy or forget and sometimes don’t comply completely with the treatment, but sooner or later the pain creeps back in. It turns out that regular chiropractic visits can actually help fibromyalgia patients adhere to long-term physical-therapy programs, thereby ensuring that patients receive the full benefits of exercise.
In a 2009 study, 55 women with fibromyalgia ages 21-59 years old were divided into two groups: some completed resistance training and the others received chiropractic adjustments in addition to doing resistance training. Both groups improved significantly with increased upper and lower body strength, decreased pain and tender points, and an improved ability to perform everyday tasks. But the patients who received chiropractic care were more likely to follow the exercise program consistently. They also had more significant improvements in functionality, balance, flexibility, and endurance.
This study confirmed the power of exercise and resistance training to ease the pain of fibromyalgia. At the same time, it demonstrates that combining chiropractic adjustments and physical therapy may enhance the benefits of both treatments.
Panton LB, Figueroa A, Kingsley JD, et al. “Effects of resistance training and chiropractic treatment in women with fibromyalgia.” Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 15.3 (2009): 321-328.
 According to the National Institutes of Health, lower back pain is the second most common form of chronic pain after headaches. Experts estimate that approximately 80% of Americans will seek help for low back pain at some point during their lives. Public health officials and insurers estimate that Americans spend $50 billion each year on treatments that are often ineffective. The standard treatment for lower back pain is to take muscle relaxants, painkillers or anti-inflammatory medications, along with physical therapy and back exercises. However, few medical interventions relieve pain reliably, and continuing to take painkillers on a long-term basis is not advised. Massage, on the other hand, has been found to be an effective way of dealing with back pain on a regular basis.
According to the National Institutes of Health, lower back pain is the second most common form of chronic pain after headaches. Experts estimate that approximately 80% of Americans will seek help for low back pain at some point during their lives. Public health officials and insurers estimate that Americans spend $50 billion each year on treatments that are often ineffective. The standard treatment for lower back pain is to take muscle relaxants, painkillers or anti-inflammatory medications, along with physical therapy and back exercises. However, few medical interventions relieve pain reliably, and continuing to take painkillers on a long-term basis is not advised. Massage, on the other hand, has been found to be an effective way of dealing with back pain on a regular basis.
Treatment for lower back pain accounts for approximately a third of all visits to a massage therapist. A study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine found that patients suffering from lower back pain of unknown origin were helped more by massage than by conventional medical treatment. Of 401 total study participants, 133 received traditional medical care with no massage, 132 received structural massage (which addresses particular muscular and skeletal structures that cause pain) and 36 received relaxation massage (a general form of massage, such as Swedish, intended for overall relaxation).
Participants in the massage groups received one hour-long massage once a week for 10 weeks. All participants completed a questionnaire at the beginning of the study, then again at 10 weeks, 24 weeks and a year after the beginning of the study to report on their perceived pain. Both kinds of massage groups reported greater pain relief and ease of motion after 10 weeks of treatment than the medical group.
An average of 37% of the patients in the massage groups reported that their pain was almost or completely gone, while only 4% of the usual care group reported similar results. This was also the case at 26 weeks. However, at the one-year mark, the benefits to all groups were about equal. The type of massage used did not seem to matter, with both massage groups experiencing comparable levels of pain relief. The massage groups were less likely to report having used medication for their back pain after the 10 weeks of intervention, and they also reported having spent fewer days in bed and had lost fewer days of work or school than those in the usual care group.
Dr. Richard A. Deyo, professor of family medicine at Oregon Health and Science University in Portland says of the study, “I think this trial is good news in the sense that it suggests that massage is a useful option that helps some substantial fraction of these patients. Like in most other treatments, this is not a slam dunk, and it’s not like a cure, but it’s something that seems to offer a significant benefit for a substantial number of patients.” Deyo sees massage as a way of people being able to break out of the pain-inactivity cycle. He notes, “I don’t see massage as the final solution, I see it as maybe a helpful step toward getting people more active.”
As always, chiropractic care shows the greatest success in the treatment of all types of back pain. We have found that chiropractic care combined with massage can be a very effective option for many of our patients. If you are currently experiencing back pain, be sure to call our office to schedule an appointment with Dr. Oblander. 406-652-3553
 Chiropractic Can Help Asthma, COPD and More…
Chiropractic Can Help Asthma, COPD and More…The World Health Organization reports that some of the most common chronic respiratory diseases include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pulmonary hypertension, the last of which is high blood pressure in the arteries connecting the heart and lungs.
Though some of these conditions can be passed down through genetics, lifestyle factors play a role as well, with risks rising with increased exposure to cigarette smoke, high levels of air pollution, and chemicals and other toxins found in various work or home environments. Obviously, your genes are your genes and removing these types of environmental toxins can go a long way to avoiding the development of lung-based diseases. Find out how Chiropractic care plays a positive roll.
One study has discovered that another way to keep your lungs breathing easier is with regular chiropractic visits. In September of 2016, the Journal of Physical Therapy Science published a study involving 30 subjects between the ages of 20 and 38 who were not currently being treated for any type of respiratory issue, nor were they experiencing any pain in their thoracic region. One-half were randomly assigned to an experimental group, which is the group that received actual spinal manipulation therapy. The remainders were assigned to the control, receiving sham treatments instead.
At the onset of the study, each subject’s respiratory function was tested and recorded. Approximately ten minutes later, depending on which group they were in, they either received high-velocity, low-amplitude manipulation directed to the thoracic area of the spine or sham chiropractic. Follow-up respiratory testing occurred immediately following the actual or sham treatment session.
After studying the lung-function data collected, researchers noted that the experimental group, which is the group that received actual chiropractic, had “significantly increased” their forced vital capacity and forced expiratory volume in one second. The group that received the sham treatments experienced no difference in their respiratory function at all.
These findings suggests that chiropractic care likely plays a more important role in healthy lung function than most people realize. This information may be helpful to patients who are already experiencing chronic respiratory issues and looking for relief, but it may also work to reduce the likelihood of lung-related diseases in the first place.
As the COPD Foundation states, generally speaking, “once lung function is gone, it is gone for good.” That’s why they recommend engaging in activities which can maximize lung capacity. These include: getting some type of regular exercise, performing physically demanding exercises during the times when it’s easier to breathe, and staying indoors when extreme temperatures are expected or pollution is high.
Article shared from the following website: https://www.chironexus.net/2017/10/chiropractic-improve-respiratory-function/

Professional Football Hall of Famer, Jerry Rice, has utilized chiropractic care throughout his legendary career in the NFL. Rice even credits chiropractic care for helping him succeed in his second career on Dancing with the Stars.
 With the huge rise in the use of antibiotics over the past 70 years, some pathogens are now becoming resistant to the drugs that once easily eradicated the illnesses these pathogens cause. People who become infected with one of these drug-resistant organisms are at increased risk for longer, more costly hospital stays and are more likely to die from their infection.
With the huge rise in the use of antibiotics over the past 70 years, some pathogens are now becoming resistant to the drugs that once easily eradicated the illnesses these pathogens cause. People who become infected with one of these drug-resistant organisms are at increased risk for longer, more costly hospital stays and are more likely to die from their infection.
Medical researchers and public health experts believe there are a few different causes for the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria. These include the widespread use of antibiotics in animals as well as and the overuse and misuse of antibiotics in humans.
Cattle, pigs and chickens are routinely given antibiotics to prevent illness and increase weight gain. However, 55 outbreaks of foodborne illness over the past 40 years have been caused by antibiotic-resistant pathogens. New York Congresswoman Louise M. Slaughter, a microbiologist, said “We have evidence that the practice of overusing antibiotics in food-animals is ruining these drugs’ effectiveness, and every day that the government stands idly by, we move closer to the nightmare scenario where routine infections can no longer be cured with antibiotic treatment.” Slaughter has proposed Preservation of Antibiotics for Medical Treatment Act (PAMTA), which would ban the use of 8 major classes of antibiotics from use on healthy animals, with exceptions only for animals who are actually ill.
Doctors are often pressured to prescribe antibiotics for illnesses that antibiotics are ineffective at treating, such as viruses. Parents of sick children have been shown to be particularly bad about exerting pressure on their doctor to give their children an antibiotic, no matter what the illness actually is. In the case of viruses (such as the one that causes the common cold, most coughs and the flu), antibiotics are useless. Antibiotics work against bacteria such as streptococcal bacteria (strep throat) and staphylococcal bacteria (skin infections). The bacterial infections most in danger of becoming resistant to all antibiotics include anthrax, gonorrhea, group B Streptococcus, Klebsiella, Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Streptococcus pneumoniae, tuberculosis, typhoid fever, vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and the antimicrobial-resistant staph bacteria VISA and VRSA.
The best way to help reduce the spread of drug-resistant illnesses is to refrain from pressuring your doctor to prescribe antibiotics when it is not appropriate, and when antibiotics are called for, to take them according to directions. Be sure to complete the full course of the antibiotic regimen prescribed, even if you are feeling well again. If you don’t, some bacteria may linger and develop a resistance to the drug you are taking, potentially making that antibiotic ineffective for you in the future. Do not skip any doses, share your antibiotics with anyone else, or use antibiotics that have been prescribed for someone else.
In general, the symptoms of a virus disappear in about a week or so. In contrast, bacterial infections tend to linger. So if you have been feeling ill for more than two weeks, consult with your physician to see if antibiotics may be appropriate for treating of your illness. If not, he or she can prescribe other effective ways to treat your condition.