Chiropractor vs. Physical Therapist: Which Type of Doctor Is Better for Treating Back Pain?
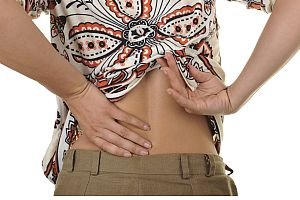
 If you’re suffering from acute or chronic back pain–whether it’s been caused by an injury or some type of medical condition–chances are that you’re more interested in finding relief NOW than learning about the many different types of doctors who are part of the healthcare community. But the simple truth is that different types of doctors tend to approach their work in particular ways because of basic differences in their training and clinical experience. This means that it’s worthwhile for a back pain patient to understand at least a little bit about how a physician’s chosen discipline can influence his or her perspective and priorities when it comes to treatment.
If you’re suffering from acute or chronic back pain–whether it’s been caused by an injury or some type of medical condition–chances are that you’re more interested in finding relief NOW than learning about the many different types of doctors who are part of the healthcare community. But the simple truth is that different types of doctors tend to approach their work in particular ways because of basic differences in their training and clinical experience. This means that it’s worthwhile for a back pain patient to understand at least a little bit about how a physician’s chosen discipline can influence his or her perspective and priorities when it comes to treatment.
The back and neck are very complex structures, and it can sometimes be difficult to identify the specific source of a patient’s pain and treat it effectively. This is why it is common for general practitioners to refer patients who are experiencing back problems more complicated than the typical muscle strain to physicians who specialize in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal disorders. Depending on the circumstances, your general practitioner may recommend a chiropractor or a physical therapist. Some cases may also benefit from a multidisciplinary or integrated care approach that draws on the expertise of multiple specialists. So, in what ways are chiropractic physicians and physical therapists similar? And how are they different?
The Chiropractor
A doctor of chiropractic diagnoses and treats disorders of the musculoskeletal and nervous systems, and works with patients to prevent disorders from occurring. This type of healthcare professional will attempt to identify the underlying cause of back pain and treat it using a variety of techniques that realign the spine to relieve pressure, restore stability and improve function. Chiropractic treatments are usually referred to as “manipulation”, “adjustment” or “mobilization”. They involve applying varying degrees of highly-targeted force (either manually or with the help of specialized instruments) to move vertebrae back into their proper position.
When a patient is experiencing acute or chronic back pain and/or has lost function, a chiropractor will also use manipulation and mobilization techniques on the joints and other soft tissues in the affected area to increase range of motion.
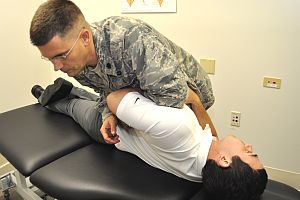
The Physical Therapist
A doctor of physical therapy also diagnoses and treats back pain, though most often in connection with a specific injury or following surgery. His or her goal is usually to help a patient regain normal function by building strength and stamina, increasing balance and flexibility, and improving coordination.
Back pain that results from injury, disease, general wear-and-tear or other environmental factors can prevent a person from being able to lead a normal life by limiting their mobility. Day-to-day activities like walking, climbing stairs and getting into or out of chairs can become difficult or impossible. For athletes, the impact can be particularly profound–limiting their ability to train and compete. A physical therapist considers how the individual’s condition is impacting their ability to move and develops a therapy program intended to improve their condition. Where the chiropractor will often use manipulation and mobilization techniques as the foundation of a treatment plan and reinforce these with structured stretching and exercise programs, the physical therapist will tend to focus more on supervised exercise.
For patients with debilitating injuries and those who have recently had surgery, both chiropractic care and physical therapy can be very good options. Well-trained and experienced doctors will provide customized treatment plans designed to help patients recover as quickly and completely as possible. The diagnostic and treatment techniques each type of doctor uses (as well as their general philosophy) may differ to some extent, but there is also substantial overlap. Both kinds of physicians use non-invasive, hands-on treatment techniques as well as high-tech therapies such as low level laser therapy (LLLT) and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) to relieve pain, reduce inflammation and accelerate healing.
When the time comes to make a decision to see one type of doctor or the other for back pain, patients often make their choice based on referrals from their primary care physician or on reviews from other patients. But the most important thing to remember is that you DO have options, and that having the RIGHT doctor matters just as much as having the right kind of doctor. We believe that our relationship with patients–especially the way we communicate–is just as important as our technical skills in diagnosing and treating your pain.
If you’d like to learn more about our approach, we invite you to call or visit our office today.

 While it seems like such a commonplace activity, shoveling snow is notorious for being one of the most dangerous things you can do in the winter. The physical exertion it involves, coupled with cold temperatures, can put excessive strain on both your heart and back. Nearly 200,000 Americans were treated in emergency rooms for conditions related to snow shoveling between 1990 and 2006.
While it seems like such a commonplace activity, shoveling snow is notorious for being one of the most dangerous things you can do in the winter. The physical exertion it involves, coupled with cold temperatures, can put excessive strain on both your heart and back. Nearly 200,000 Americans were treated in emergency rooms for conditions related to snow shoveling between 1990 and 2006.