Chiropractic Safer than Medical Care for Elderly
 Many studies have found that chiropractic care is a safe and effective treatment method when dealing with a number of spine-related issues. The American Chiropractic Association even lists a number of research studies on their website that show that it is a valuable treatment method for easing (and sometimes completely resolving) back pain, neck pain, headaches, and more.
Many studies have found that chiropractic care is a safe and effective treatment method when dealing with a number of spine-related issues. The American Chiropractic Association even lists a number of research studies on their website that show that it is a valuable treatment method for easing (and sometimes completely resolving) back pain, neck pain, headaches, and more.
While all of this is good news for professionals that practice in the chiropractic field, some researchers wondered if chiropractic was just as safe for elderly patients as it is for younger patients experiencing these types of problems. So, they set out to find the answer, which they did via a retrospective cohort study funded by NIH and the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine, and also which was subsequently printed in Spine upon its completion.
What researchers wanted to discover was whether the relationship between the risk of injury to people 66 years old and older when engaging in chiropractic care was higher than, lower than, or equal to the risk of injury to this same age group after undergoing medical care by their primary care physician. To find their answer, they studied data on Medicare B patients who went to the doctor in 2007 for a neuromusculoskeletal issue, evaluating their risk of injury seven days post-treatment.
They discovered that seniors that received chiropractic care had a 76% lower rate of injury within seven days of treatment when compared to the subjects that met with their primary physician as a result of a neuromusculoskeletal complaint. Researchers also pointed out that they found that males contained within the research group, older study participants, and those with a higher Charlson co-morbidity score were most at risk of injury within the week after acquiring a neuromusculoskeletal issue.
Additionally, certain medical conditions raised the risk of injury, even after chiropractic care. Therefore, chiropractic professionals should consider whether treatment via spinal manipulation is best for “patients with coagulation defects, inflammatory spondylopathy, osteoporosis, aortic aneurysm & dissection, or [those who have engaged in] long term use of anticoagulant therapy” as the increased risk may not be worth the benefits.
Whedon JM, Mackenzie TA, Phillips RB, Lurie JD. Risk of traumatic injury associated with chiropractic spinal manipulation. Spine 2014;Dec 9.
 Countless studies have demonstrated that chiropractic care is a safe and effective way to treat musculoskeletal complaints like back pain, neck pain, or sciatica. Now a new study from Switzerland has looked at the relative benefits of chiropractic compared to medical care for the most common types of pain issues.
Countless studies have demonstrated that chiropractic care is a safe and effective way to treat musculoskeletal complaints like back pain, neck pain, or sciatica. Now a new study from Switzerland has looked at the relative benefits of chiropractic compared to medical care for the most common types of pain issues. Sciatica pain is often so debilitating that it forces people to miss work and other normal activities. Of all patients with low-back pain, sciatica patients have the highest level of disability (1). In fact, patients with sciatica are disabled for an average of 72 days according to Norwegian public-health records.
Sciatica pain is often so debilitating that it forces people to miss work and other normal activities. Of all patients with low-back pain, sciatica patients have the highest level of disability (1). In fact, patients with sciatica are disabled for an average of 72 days according to Norwegian public-health records. Back pain is an expensive health problem for both patients and businesses.
Back pain is an expensive health problem for both patients and businesses.  We recently posted about standing desks. For those of you who are looking for some good information on standing desks, today we are sharing a review on some standing desks. Standing desks are a great option where they are allowed! Standing desks can be of great benefit by allowing greater circulation while you are working at your desk! Wonderful for those of us who spend a considerable amount of time sitting at a desk!
We recently posted about standing desks. For those of you who are looking for some good information on standing desks, today we are sharing a review on some standing desks. Standing desks are a great option where they are allowed! Standing desks can be of great benefit by allowing greater circulation while you are working at your desk! Wonderful for those of us who spend a considerable amount of time sitting at a desk!


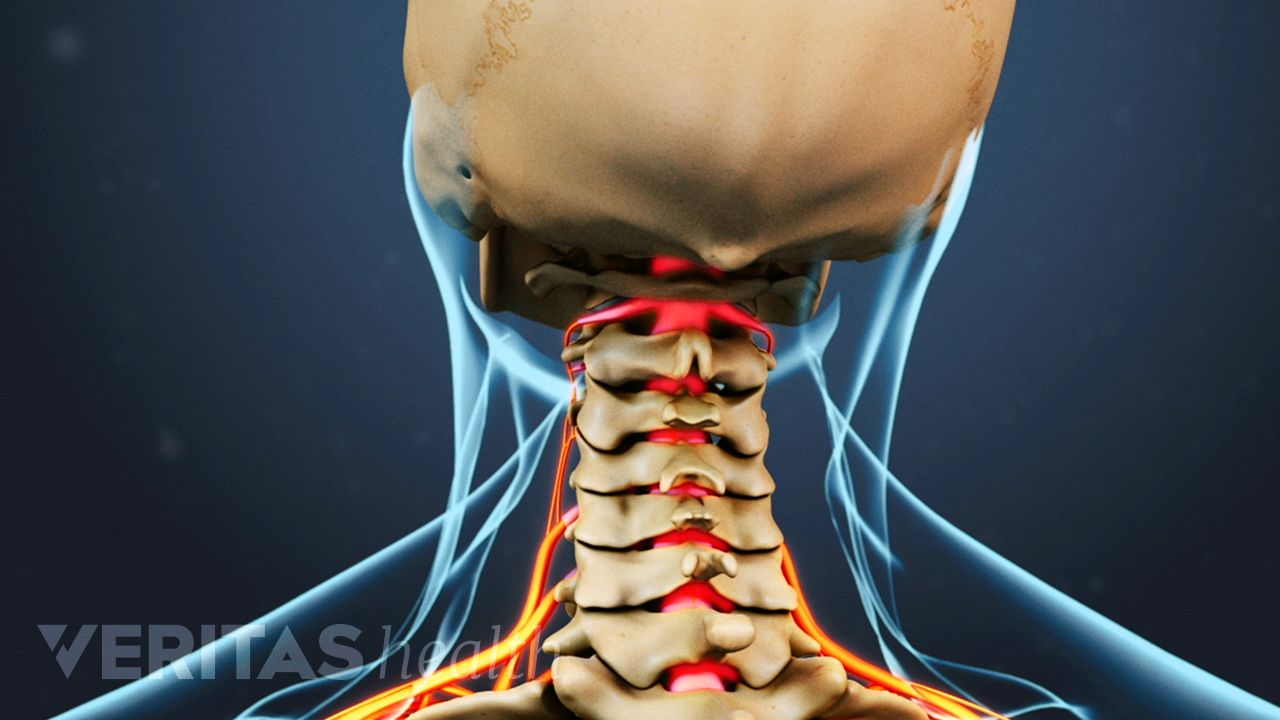
 Most people at some point have heard cracking or grinding noises in their neck upon movement. These sounds, also called crepitus, are usually painless and typically do not represent anything serious.
Most people at some point have heard cracking or grinding noises in their neck upon movement. These sounds, also called crepitus, are usually painless and typically do not represent anything serious.