Chiropractic Treatments for Whiplash
.Because each individual case of whiplash is different, it is not possible to generalize about the chiropractic whiplash treatment.
The appropriate chiropractic treatment is unique to each whiplash injury and is directed at the primary dysfunctions detected during the chiropractic exam.
However, chiropractors commonly employ different chiropractic treatments for whiplash, often including:
- Manipulation
- Muscle relaxation and/or stimulation
- Various exercises
- Ergonomic and lifestyle changes.
This article explains when, why and how chiropractors may employ these whiplash treatments for neck pain, shoulder pain, back pain, and other related symptoms.
Chiropractic Manipulation for Whiplash
The primary whiplash treatment for joint dysfunction, spinal manipulation involves the chiropractor gently moving the involved joint into the direction in which it is restricted.
Also known as a chiropractic adjustment, spinal manipulation may involve the application of a short thrust in that direction. In many cases, instead of a thrust, a slow mobilizing movement is used by the chiropractor.
Muscle Relaxation or Stimulation as Whiplash Treatments
The chiropractor’s primary whiplash treatment for related muscle dysfunction, muscle relaxation and/or stimulation consist of gentle stretches to the muscle that has excessive tension or repeated contractions of the muscle that is inhibited.
If the muscle is very tight, a more vigorous stretch may be applied by the chiropractor. Gentle finger pressure techniques may be applied to trigger points to relieve the pain associated with the tight muscles.
McKenzie Exercises and Stabilization/Sensorimotor Activities
Chiropractors may employ different types of exercises, including McKenzie exercises and/or stabilization and sensorimotor exercises, to help treat patients with whiplash injuries.
McKenzie exercises are specifically designed to reduce disc derangement related to a whiplash injury. They consist of simple movements that are initially done in the office but make for an easy transition to self-care at home. McKenzie exercises also help the patient take an active role in his or her own recovery.
Stabilization and sensorimotor exercise approaches are designed to correct faulty movement patterns in routine activities and everyday life. Such whiplash treatment trains the nervous system to better coordinate and control movement patterns and improves the ability of the neck muscles to maintain stability of the neck.
These exercises are designed to help in a major trauma, such as a fall or whiplash during a motor vehicle accident, or in “microtrauma” from simple things such as being jostled in a crowd, playing sports or performing occupational or home jobs that require physical effort.
Chiropractic Advice on Ergonomic and Lifestyle Changes
These whiplash treatment suggestions stress improvements for performing everyday activities with minimal strain to the body. The chiropractic advice addresses factors in an individual’s work, home or recreational activities that perpetuate the dysfunctions that result from the whiplash accident.
Additionally, spine care professionals at the chiropractic clinic may teach the patient better “use of self” and, if necessary, stress reduction methods to help chiropractic problems.
Whiplash Treatment in Chiropractic Care
The whiplash treatment plan developed by the chiropractor for each specific problem may include one or more of these approaches and may involve others as well.
In addition to his or her whiplash treatment plan, the doctor of chiropractic might give a referral to another health professional, such as a medical specialist if it is deemed appropriate.
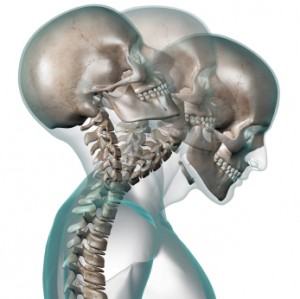
Today’s article was written by Donald Murphy, DC and is shared from the following website: https://www.spine-health.com/treatment/chiropractic/chiropractic-treatments-whiplash. Today’s image was shared from the following website: https://seriousaccidents.com/personal-injury/whiplash-injuries/
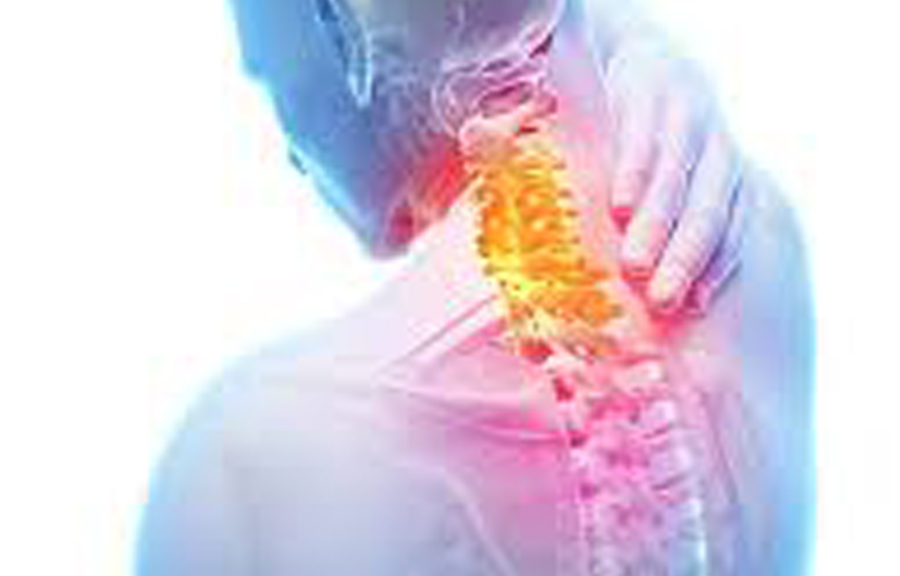
 Perhaps the most frequent injury involving automobiles comes from closing the door. Nearly 150,000 times a year, someone is injured in this fashion, and that’s with the car parked or stationary. This includes doors closing on fingers. Another 10,000 are injured by using a jack and 74,000 have been injured by a car or car part falling on them.
Perhaps the most frequent injury involving automobiles comes from closing the door. Nearly 150,000 times a year, someone is injured in this fashion, and that’s with the car parked or stationary. This includes doors closing on fingers. Another 10,000 are injured by using a jack and 74,000 have been injured by a car or car part falling on them.