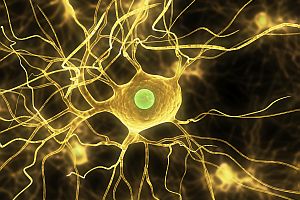
Chiropractic Care and Your Sympathetic Nervous System
While chiropractic physicians are generally thought of as experts in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal problems (particularly those related to back and neck pain), chiropractic treatments can also help the body’s nervous system function more effectively. From freeing pinched nerves and relieving generalized pain to regulating the immune system and stimulating healing, chiropractic care can achieve a wide range of long-lasting health benefits.
To understand how chiropractic care can have these broader benefits, it’s useful to know a little bit about how your nervous system works. Doctors use a few different frameworks for describing the structure and function of the nervous system. One of the most basic frameworks distinguishes between your autonomic nervous system (ANS) or “involuntary” nervous system and your somatic nervous system (SoNS) or “voluntary” nervous system. The remainder of this article is about the two main branches of the ANS, the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
The body’s autonomic nervous system is actually made up of three parts—the sympathetic nervous system, the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. All of these parts work together to act as a control system that regulates the functions of the internal organs, such as the heart, stomach and intestines. From a structural point of view, the ANS operates as a complex network of neurons that originates inside the spinal cord and extends throughout the body via a series of interconnected hubs (called “ganglia” or “trunks”).
The ANS is active at all times and is responsible for unconscious regulation of our glands and organs. In very general terms, the sympathetic nervous system regulates the “fight or flight” responses during times of stress or anxiety, including increased awareness, heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate and sweating. In contrast, the parasympathetic nervous system coordinates processes associated with the “rest and recover” or “rest and digest” responses, such as salivation, tears, sexual arousal and digestion.
The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems have a complementary, push-pull relationship that allows the body to respond very swiftly when necessary (through the sympathetic nervous system’s quick mobilization) and to slow down to perform other, less urgent activities in the background when appropriate (through the parasympathetic nervous system’s more gradual dampening). Together, these systems act a bit like an accelerator and a brake for our bodies and also help to maintain balance, or “homeostasis.”
During the fight or flight response, your body slows or shuts down many of the rest and repair processes so that more energy is available for the processes necessary for near-term survival. In nonemergency situations, the parasympathetic nervous system is supposed to go to work, conserving energy and directing it to rest and repair responses, including healing. This is where chiropractic care can be very helpful.
While stress hormones and the physiological changes they trigger can be helpful (maybe even life-saving) when we’re facing real physical threats, they can do significant damage to our health over the long term if they’re switched on all the time. Certain types of chiropractic adjustments have been shown to affect the autonomic nervous system by helping to down-regulate the sympathetic nervous system and stimulate parasympathetic activity. Quieting the fight or flight responses in turn promotes healing, bolsters the immune system and helps relieve the immediate sensation of pain.
There’s no doubt that chiropractors can help patients find relief from acute injuries and chronic musculoskeletal conditions. But we may also be able to help you address neurological problems. If you’re interested in learning more, we encourage you to call or visit the office today!
Additional Resources
Sympathetic and parasympathetic responses to specific diversified adjustments to chiropractic vertebral subluxations of the cervical and thoracic spine. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2686395/
Short-term effects of cervical manipulation on edge light pupil cycle time: A pilot study. http://www.jmptonline.org/article/S0161-4754%2800%2981597-3/abstract
Hormones: Chemical Messengers and the Chiropractic Link. http://www.theamericanchiropractor.com/articles-integrative-healthcare/4895-hormones-chemical-messengers-and-the-chiropractic-link.html
 Palpation is the most frequently used diagnostic technique in chiropractic care and is a clinical cornerstone of most physicians’ practice. It is a manual, non-invasive method of determining where a patient has structural or functional problems in the body.
Palpation is the most frequently used diagnostic technique in chiropractic care and is a clinical cornerstone of most physicians’ practice. It is a manual, non-invasive method of determining where a patient has structural or functional problems in the body.
 As we age, the discs in our spine start to naturally break down due to normal, everyday living . This is commonly referred to as disc degeneration and can result in pain in the neck and/or back area–pain that is felt by almost half of the population 40 years of age or older . For those over 80, this rate doubles to a whopping 80 percent, which makes understanding what factors promote this particular condition critical to raising the quality of life as we enter
As we age, the discs in our spine start to naturally break down due to normal, everyday living . This is commonly referred to as disc degeneration and can result in pain in the neck and/or back area–pain that is felt by almost half of the population 40 years of age or older . For those over 80, this rate doubles to a whopping 80 percent, which makes understanding what factors promote this particular condition critical to raising the quality of life as we enter