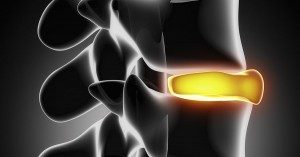
 As we age, the discs in our spine start to naturally break down due to normal, everyday living . This is commonly referred to as disc degeneration and can result in pain in the neck and/or back area–pain that is felt by almost half of the population 40 years of age or older . For those over 80, this rate doubles to a whopping 80 percent, which makes understanding what factors promote this particular condition critical to raising the quality of life as we enter our later years. Fortunately, recent research provides some very important information in this area.
As we age, the discs in our spine start to naturally break down due to normal, everyday living . This is commonly referred to as disc degeneration and can result in pain in the neck and/or back area–pain that is felt by almost half of the population 40 years of age or older . For those over 80, this rate doubles to a whopping 80 percent, which makes understanding what factors promote this particular condition critical to raising the quality of life as we enter our later years. Fortunately, recent research provides some very important information in this area.
Disc Degeneration Risk Factors Revealed In Recent Study
On November 9, 2015, a study conducted by health experts from Mie University Graduate School of Medicine in Japan, Osaka University (also in Japan), and Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, Illinois was published in BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. In this research, these experts followed 197 individuals living in Miyagawa, Japan who were over the age of 65 for a 10-year period, measuring their disc height at two year intervals to determine what factors, if any, contributed to their spinal discs degenerating at a faster rate.
What they discovered was that, over the time span of the study, the participants’ disc height gradually reduced an average of 5.8 percent, with roughly 55 percent experiencing degeneration in one or two of their discs. Furthermore, there were three factors that they identified that increased the likelihood of disc degeneration. They were: 1) being female, 2) having radiographic knee osteoarthritis, and 3) the presence of low back pain when the study began.
Based on these results, women should take extra care to protect the discs in their spinal column, potentially saving themselves from experiencing neck or back pain later in life. Some options for doing this include maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding repeated lifting of heavy objects, and not smoking as studies have found that smokers tend to experience disc degeneration at greater rates than non-smokers . Chiropractic can help with the other two factors.
For instance, in one study published in The Journal of the Canadian Chiropractic Association, researchers looked at 43 different individuals between the ages of 47 and 70 who were experiencing osteoarthritic knee pain. Some participants received treatment three times a week for two weeks and others served as a control. The subjects who engaged in treatment reported more positive results than those who did not, citing that, after the treatments they experienced fewer osteoarthritic symptoms, had greater knee mobility, and felt that it was easier to “perform general activities.” And this was after just two weeks of care.
Chiropractic can also help lower back pain, further reducing the likelihood that your discs will degenerate at a faster rate when you age. That makes this specific remedy beneficial both now and well into the future–ultimately raising your quality of life. If you need to see Dr. Oblander for an adjustment, please be sure to give our office a call at 406-652-3553!
- Akeda K, Yamada T, Inoue N, et al. Risk factors for lumbar intervertebral disc height narrowing: a population-based longitudinal study in the elderly. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2015;16(1):344.
- Fogelholm RR, Alho AV. Smoking and intervertebral disc degeneration. Medical Hypotheses; 56(4):537-9.
- Pollard H, Ward G, Hoskins W, Hardy K. The effect of a manual therapy knee protocol on osteoarthritic knee pain: a randomised controlled trial. Journal of the Canadian Chiropractic Associations 2008;52(4):229-42.
Written by: Christina DeBusk
Article shared from Chironexus.net
 y times did you hear, “Sit up straight!” as a child? How many times have you said this to your own child? There’s a reason behind that famous advice: poor posture early in life may lead to a number of back problems and pain later on. That’s why researchers conducted a study to better understand slouching in adolescents.
y times did you hear, “Sit up straight!” as a child? How many times have you said this to your own child? There’s a reason behind that famous advice: poor posture early in life may lead to a number of back problems and pain later on. That’s why researchers conducted a study to better understand slouching in adolescents. Anyone with a chronic pain condition like fibromyalgia knows it can be difficult to adhere to a complex set of treatment instructions: physical therapy, medications, creams, journals, the list goes on. We get busy or forget and sometimes don’t comply completely with the treatment, but sooner or later the pain creeps back in. It turns out that regular chiropractic visits can actually help fibromyalgia patients adhere to long-term physical-therapy programs, thereby ensuring that patients receive the full benefits of exercise.
Anyone with a chronic pain condition like fibromyalgia knows it can be difficult to adhere to a complex set of treatment instructions: physical therapy, medications, creams, journals, the list goes on. We get busy or forget and sometimes don’t comply completely with the treatment, but sooner or later the pain creeps back in. It turns out that regular chiropractic visits can actually help fibromyalgia patients adhere to long-term physical-therapy programs, thereby ensuring that patients receive the full benefits of exercise. According to the National Institutes of Health, lower back pain is the second most common form of chronic pain after headaches. Experts estimate that approximately 80% of Americans will seek help for low back pain at some point during their lives. Public health officials and insurers estimate that Americans spend $50 billion each year on treatments that are often ineffective. The standard treatment for lower back pain is to take muscle relaxants, painkillers or anti-inflammatory medications, along with physical therapy and back exercises. However, few medical interventions relieve pain reliably, and continuing to take painkillers on a long-term basis is not advised. Massage, on the other hand, has been found to be an effective way of dealing with back pain on a regular basis.
According to the National Institutes of Health, lower back pain is the second most common form of chronic pain after headaches. Experts estimate that approximately 80% of Americans will seek help for low back pain at some point during their lives. Public health officials and insurers estimate that Americans spend $50 billion each year on treatments that are often ineffective. The standard treatment for lower back pain is to take muscle relaxants, painkillers or anti-inflammatory medications, along with physical therapy and back exercises. However, few medical interventions relieve pain reliably, and continuing to take painkillers on a long-term basis is not advised. Massage, on the other hand, has been found to be an effective way of dealing with back pain on a regular basis. Chiropractic Can Help Asthma, COPD and More…
Chiropractic Can Help Asthma, COPD and More… Learning the risk factors of sciatica can help you minimize your risk of developing it. A recent study sheds light onto what makes you more likely to develop sciatica.
Learning the risk factors of sciatica can help you minimize your risk of developing it. A recent study sheds light onto what makes you more likely to develop sciatica. With the huge rise in the use of antibiotics over the past 70 years, some pathogens are now becoming resistant to the drugs that once easily eradicated the illnesses these pathogens cause. People who become infected with one of these drug-resistant organisms are at increased risk for longer, more costly hospital stays and are more likely to die from their infection.
With the huge rise in the use of antibiotics over the past 70 years, some pathogens are now becoming resistant to the drugs that once easily eradicated the illnesses these pathogens cause. People who become infected with one of these drug-resistant organisms are at increased risk for longer, more costly hospital stays and are more likely to die from their infection. Most teens experience headaches at some point and many will suffer the debilitating impact of persistent headaches or migraines. Chronic headaches can prevent teens from engaging fully in school, work, and extracurricular activities. Yet little was known about what triggers headaches in teens until now.
Most teens experience headaches at some point and many will suffer the debilitating impact of persistent headaches or migraines. Chronic headaches can prevent teens from engaging fully in school, work, and extracurricular activities. Yet little was known about what triggers headaches in teens until now. As we age, the discs in our spine start to naturally break down due to normal, everyday living . This is commonly referred to as disc degeneration and can result in pain in the neck and/or back area–pain that is felt by almost half of the population 40 years of age or older . For those over 80, this rate doubles to a whopping 80 percent, which makes understanding what factors promote this particular condition critical to raising the quality of life as we enter
As we age, the discs in our spine start to naturally break down due to normal, everyday living . This is commonly referred to as disc degeneration and can result in pain in the neck and/or back area–pain that is felt by almost half of the population 40 years of age or older . For those over 80, this rate doubles to a whopping 80 percent, which makes understanding what factors promote this particular condition critical to raising the quality of life as we enter  People are becoming increasingly aware of the dangers that can result from the overuse of antibiotics. When antibiotics were first discovered in the early 20th century, researchers believed that they had found the key to conquering many deadly diseases. Since that time, antibiotics have certainly helped to cure diseases that once wiped out large parts of the population. However, there is growing evidence that antibiotics are now being used too frequently, and that they are often being used in inappropriate circumstances. This has led to many previously curable diseases becoming antibiotic-resistant, which means that a cure now requires the use far stronger antibiotics. In fact, some diseases have now become resistant to nearly all antibiotics. It is obvious that if antibiotic use continues in this way, we may have a major health crisis on our hands.
People are becoming increasingly aware of the dangers that can result from the overuse of antibiotics. When antibiotics were first discovered in the early 20th century, researchers believed that they had found the key to conquering many deadly diseases. Since that time, antibiotics have certainly helped to cure diseases that once wiped out large parts of the population. However, there is growing evidence that antibiotics are now being used too frequently, and that they are often being used in inappropriate circumstances. This has led to many previously curable diseases becoming antibiotic-resistant, which means that a cure now requires the use far stronger antibiotics. In fact, some diseases have now become resistant to nearly all antibiotics. It is obvious that if antibiotic use continues in this way, we may have a major health crisis on our hands. If you are like most people, working out just for the sake of working out does not really appeal (although there are many dedicated gym buffs who couldn’t live without their daily workouts!). We all know that it’s important to exercise regularly if we want to live a long and healthy life. However, if you find the idea of trotting along on a treadmill for 15 minutes and then spending half an hour of working out on Nautilus machines to be about as exciting as a trip to the dentist, then this article is for you!
If you are like most people, working out just for the sake of working out does not really appeal (although there are many dedicated gym buffs who couldn’t live without their daily workouts!). We all know that it’s important to exercise regularly if we want to live a long and healthy life. However, if you find the idea of trotting along on a treadmill for 15 minutes and then spending half an hour of working out on Nautilus machines to be about as exciting as a trip to the dentist, then this article is for you!