When it Comes to Posture, the Little Things Matter. Like Sitting on Your Wallet…

You know the big things that impact your posture, such as the height of your keyboard or whether you slouch on the couch, but it’s easy to overlook the little things. By the way, where is your wallet right now? If it’s currently in your back pocket, we need to have a talk…
Little Things Matter When it Comes to Posture
Your wallet fits so perfectly in your back pocket. Certainly it can’t hurt to keep it there, right? Unfortunately, sitting on your wallet can cause a host of posture problems, which can lead to pain in your back, shoulders, and neck. When half of your posterior is higher than the other, your pelvis twists, the spine becomes misaligned, and your shoulders have a tendency to slump. This isn’t good, but there is a simple solution: just keep your wallet in the front!
Now that your wallet is in the right place, it’s time to look at your feet. What kind of shoes are you wearing? If you’re a woman wearing high heels, think about giving your back a break. Tall heels put you off balance, which your body compensates for by flexing at the hips and spine. The forward curve in your lower back decreases, your knees are stressed, and the muscles in your back, hips, and calves tense. All of this can lead to poor posture and back pain. Switch to flats to solve the problem.
Guys, you aren’t off the hook in the footwear department. If it’s been a while since you’ve bought a new pair of shoes, take a closer look at your soles. Wear and tear in this area can throw off your gait, leading to posture issues and—you guessed it—back pain. Maybe it’s time for some replacements…
Women with large breasts might find it particularly difficult to maintain proper posture. This is more likely to be true without the support of a proper bra. If this situation is causing you to slouch or experience back or shoulder pain, consider looking into a posture bra. These bras have bands that are designed to carry your chest’s weight, reducing pull on the shoulder straps and allowing you to sit or stand straight and without strain.
Do you carry a heavy bag or purse with you? If you’re constantly carrying a heavy weight on one side of your body, you are also constantly shifting to the side to compensate, which can lead to back pain and even nerve trauma. Take some time to clean out your bag, and try to alternate the side you carry it on to reduce the damage.
Correcting the Damage
Life is full of little things that can lead to poor posture and pain, many of which you might not be aware of. Consulting with a chiropractor can help you gain a better understanding of how your daily life affects the way you sit and stand. If your posture has already been compromised or you are already experiencing back or neck pain, chiropractic care can also help to correct it. With expert guidance and a few changes, little problems can stop being a big deal.


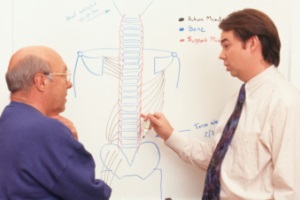 According to the National Institutes of Health and Dr. Michael S. Wilkes of the Western Journal of Medicine, “Despite a plethora of research intended to guide physicians in their management of back pain, physicians still hold strong non-evidence based beliefs dating back to the 19th century.” What beliefs is Dr. Wilkes referring to? He’s talking about the long-held conventional wisdom that says bed rest is one of the best ways to treat back pain.
According to the National Institutes of Health and Dr. Michael S. Wilkes of the Western Journal of Medicine, “Despite a plethora of research intended to guide physicians in their management of back pain, physicians still hold strong non-evidence based beliefs dating back to the 19th century.” What beliefs is Dr. Wilkes referring to? He’s talking about the long-held conventional wisdom that says bed rest is one of the best ways to treat back pain.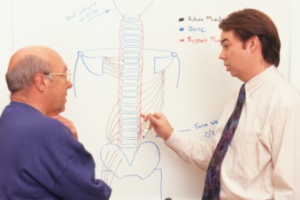 According to the National Institutes of Health and Dr. Michael S. Wilkes of the Western Journal of Medicine, “Despite a plethora of research intended to guide physicians in their management of back pain, physicians still hold strong non-evidence based beliefs dating back to the 19th century.” What beliefs is Dr. Wilkes referring to? He’s talking about the long-held conventional wisdom that says bed rest is one of the best ways to treat back pain.
According to the National Institutes of Health and Dr. Michael S. Wilkes of the Western Journal of Medicine, “Despite a plethora of research intended to guide physicians in their management of back pain, physicians still hold strong non-evidence based beliefs dating back to the 19th century.” What beliefs is Dr. Wilkes referring to? He’s talking about the long-held conventional wisdom that says bed rest is one of the best ways to treat back pain. America’s roads have become far safer across the past three decades. By just about any measure, travelers are much less likely to be injured or killed in a motor vehicle accident than they were in the late 1980s and early 1990s. And this is true even though we’re driving more miles each year!
America’s roads have become far safer across the past three decades. By just about any measure, travelers are much less likely to be injured or killed in a motor vehicle accident than they were in the late 1980s and early 1990s. And this is true even though we’re driving more miles each year!


