 Manual therapies have been used to treat musculoskeletal disorders for thousands of years. Practitioners around the world—in countries with many different cultural influences and diverse medical traditions—have used their hands to manipulate various parts of the body to stimulate healing. “Manual” literally means “by hand.” Thus, manual therapies consist of healing techniques that use the hands. There are more than two dozen techniques used worldwide. Among the most commonly known are acupressure, chiropractic, massage therapy, physiotherapy, reflexology, Rolfing and shiatsu.
Manual therapies have been used to treat musculoskeletal disorders for thousands of years. Practitioners around the world—in countries with many different cultural influences and diverse medical traditions—have used their hands to manipulate various parts of the body to stimulate healing. “Manual” literally means “by hand.” Thus, manual therapies consist of healing techniques that use the hands. There are more than two dozen techniques used worldwide. Among the most commonly known are acupressure, chiropractic, massage therapy, physiotherapy, reflexology, Rolfing and shiatsu.
There are also dozens of other, lesser-known manual therapies, including the Bowen technique, cranio-sacral therapy, the Dorn method, manual lymphatic drainage, muscle energy technique, myofascial release, myotherapy, naprapathy and zero balancing. We examine the most common therapies here:
Acupressure
Using the hand, the elbow or various devices, an acupressure practitioner applies a light force on various parts of the body following the patterns found in traditional Chinese medicine and acupuncture. More than half of the scientific studies on acupressure showed that this technique was effective, but some critics have claimed “a significant likelihood of bias.”
Chiropractic
Most chiropractic work involves manipulation of the spine to achieve better vertebral alignment. Lower back pain is perhaps the primary complaint which leads patients to a chiropractor. Chiropractors are expert at treating musculoskeletal conditions without the use of drugs or surgery. Among others, many top athletes swear by their chiropractor’s hands to keep them performing at their best and help them avoid injuries.
Massage Therapy
This is perhaps the oldest of the manual therapies. Massage was (and still is) used in ancient Egypt, China, Mesopotamia, and other parts of the world that gave rise to early civilizations. Massage practitioners chiefly use their hands, but also other parts of their body to apply pressure, rolling motions and other techniques to muscles and joints, to stimulate circulation and relax the patient. In today’s high-stress world, massage is proving ever more popular.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy has been used for years as standard treatment for patients suffering from musculoskeletal conditions. A physical therapist uses a variety of techniques to help their patients regain function—particularly mobility. Repetitive, assisted motion can help the patient strengthen muscles that have been damaged through injury or disease. Assisting the patient in the performance of targeted exercises can help a patient regain greater range of motion.
Reflexology
A trained reflexologist applies pressure to various parts of the feet, hands or ears to stimulate organs within the body associated with the part to which pressure is being applied. It is a Chinese therapy with a philosophy that is similar to acupuncture—using points on the body to restore energy flow. Although there is not yet much scientific evidence to support its effectiveness, anecdotal evidence shows that patients are happier and more relaxed after treatment.
Rolfing Structural Integration
Rolfing specifically targets the body’s connective tissue to release tension, realign and balance the body. Rolfing techniques involve deep-tissue massage to achieve therapeutic benefits such as better posture and greater freedom of movement, including reducing stress and relieving pain.
Shiatsu
A traditional Japanese therapy, the term Shiatsu means “finger pressure,” but can include palm pressure and other approaches to massage. A Shiatsu practitioner uses touch, comfortable pressure and manipulative techniques on specific points of the body (similar to the meridians of Traditional Chinese Medicine) to adjust the body’s physical structure and balance its energy flow. Anecdotal evidence shows it to relieve patients of stress, nausea, muscle pain, depression and anxiety.
 Learning the risk factors of sciatica can help you minimize your risk of developing it. A recent study sheds light onto what makes you more likely to develop sciatica.
Learning the risk factors of sciatica can help you minimize your risk of developing it. A recent study sheds light onto what makes you more likely to develop sciatica.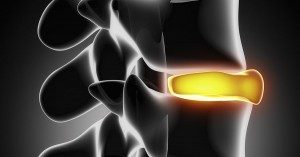 As we age, the discs in our spine start to naturally break down due to normal, everyday living . This is commonly referred to as disc degeneration and can result in pain in the neck and/or back area–pain that is felt by almost half of the population 40 years of age or older . For those over 80, this rate doubles to a whopping 80 percent, which makes understanding what factors promote this particular condition critical to raising the quality of life as we enter
As we age, the discs in our spine start to naturally break down due to normal, everyday living . This is commonly referred to as disc degeneration and can result in pain in the neck and/or back area–pain that is felt by almost half of the population 40 years of age or older . For those over 80, this rate doubles to a whopping 80 percent, which makes understanding what factors promote this particular condition critical to raising the quality of life as we enter  Countless studies have demonstrated that chiropractic care is a safe and effective way to treat musculoskeletal complaints like back pain, neck pain, or sciatica. Now a new study from Switzerland has looked at the relative benefits of chiropractic compared to medical care for the most common types of pain issues.
Countless studies have demonstrated that chiropractic care is a safe and effective way to treat musculoskeletal complaints like back pain, neck pain, or sciatica. Now a new study from Switzerland has looked at the relative benefits of chiropractic compared to medical care for the most common types of pain issues. Back pain is an expensive health problem for both patients and businesses.
Back pain is an expensive health problem for both patients and businesses.  Manual therapies have been used to treat musculoskeletal disorders for thousands of years. Practitioners around the world—in countries with many different cultural influences and diverse medical traditions—have used their hands to manipulate various parts of the body to stimulate healing. “Manual” literally means “by hand.” Thus, manual therapies consist of healing techniques that use the hands. There are more than two dozen techniques used worldwide. Among the most commonly known are acupressure, chiropractic, massage therapy, physiotherapy, reflexology, Rolfing and shiatsu.
Manual therapies have been used to treat musculoskeletal disorders for thousands of years. Practitioners around the world—in countries with many different cultural influences and diverse medical traditions—have used their hands to manipulate various parts of the body to stimulate healing. “Manual” literally means “by hand.” Thus, manual therapies consist of healing techniques that use the hands. There are more than two dozen techniques used worldwide. Among the most commonly known are acupressure, chiropractic, massage therapy, physiotherapy, reflexology, Rolfing and shiatsu. Perhaps the most frequent injury involving automobiles comes from closing the door. Nearly 150,000 times a year, someone is injured in this fashion, and that’s with the car parked or stationary. This includes doors closing on fingers. Another 10,000 are injured by using a jack and 74,000 have been injured by a car or car part falling on them.
Perhaps the most frequent injury involving automobiles comes from closing the door. Nearly 150,000 times a year, someone is injured in this fashion, and that’s with the car parked or stationary. This includes doors closing on fingers. Another 10,000 are injured by using a jack and 74,000 have been injured by a car or car part falling on them.
 We are sharing an article today that was first run in the Billings Gazette in 2014. We think it has some good information and we have added a few tips of our own at the conclusion of the article:
We are sharing an article today that was first run in the Billings Gazette in 2014. We think it has some good information and we have added a few tips of our own at the conclusion of the article: Even if your recent fender bender didn’t seem too serious, there’s still a very real chance that you or your passengers may have been hurt. That’s because even the most minor car accidents can cause hidden injuries and delayed symptoms. And while damage to your car is likely obvious and easy to assess, evaluating damage to your body may be far more difficult. In fact, it’s not unusual for a driver or passenger to walk away from a collision with potentially serious musculoskeletal injuries (such as a concussion or whiplash), without knowing it.
Even if your recent fender bender didn’t seem too serious, there’s still a very real chance that you or your passengers may have been hurt. That’s because even the most minor car accidents can cause hidden injuries and delayed symptoms. And while damage to your car is likely obvious and easy to assess, evaluating damage to your body may be far more difficult. In fact, it’s not unusual for a driver or passenger to walk away from a collision with potentially serious musculoskeletal injuries (such as a concussion or whiplash), without knowing it.