Are Stand-Up Desks Really Any Healthier for Office Workers?

Standing desks or stand-up desks are not a new fad. They’ve been around since at least the time of Benjamin Franklin, the founding father who used one over two hundred years ago. However, there remains a great deal of controversy regarding the benefits and drawbacks of stand-up desks.
A number of sources agree that standing up while you work gives you more energy and keeps you more alert. The University of Chester performed a study in 2013 that showed heartbeats rose by ten beats per minute because of standing. This increased the number of calories burned each day. In addition, blood glucose levels after lunch returned to normal far faster in those study subjects who stood as they worked.
Others have found that standing helps reduce lower back pain. Users of stand-up desks found that they engaged more fully with their colleagues and felt more ready for action if something called them away from their desk. They felt their minds wandered far less and they stayed more focused. Some users even found that stand-up desks lent themselves to certain “power poses” that benefited physiology, increasing testosterone and decreasing cortisol, the stress hormone.
Stand-up desk users seemed to agree, though, that leg and foot soreness can be a problem. This may be a particular problem for individuals who are just starting to use a stand-up desk user and whose bodies aren’t yet accustomed to the new way of working. More comfortable shoes and an anti-fatigue mat can help reduce this problem. Gradually building up the amount of time spent at a stand-up desk can also help.
If you do opt for a stand-up desk, it’s important to get one at the right height. Because each person is different, getting a custom desk built can be prohibitively expensive. A better alternative is to get an adjustable desk. One with hydraulic power can be lowered for occasional sitting and increased to a custom height to suit your individual needs.
Sitting for long periods each day can lead to all manner of illnesses—heart disease, diabetes, vein disease and more. But standing for long periods can also create health risks, especially vein disease.
A Cornell University ergonomics team found that the real solution was simply to move around regularly. If you’re sitting at a desk, stand up every 20–30 minutes and move around for two minutes. The movement gets the blood pumping, increases calorie burn, and decreases the risks for heart disease, diabetes and other ailments. This doesn’t require vigorous exercise. Simply pacing for a couple of minutes will be enough to undo the damage of sitting for half an hour. This, of course, requires an awareness of the time and a measure of discipline to move when the appointed time arrives. Adding some moderate exercise to your daily routine can do wonders for your health, even without the use of a stand-up desk.



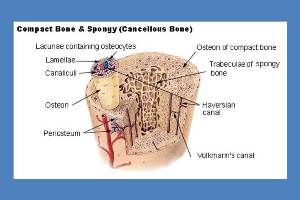 Each of the 206 bones in your body is constantly undergoing a process of breakdown and renewal, even if you have never suffered a broken bone in your life. Your entire skeleton is completely replaced approximately every 10 years. The construction of bone tissue begins when we are a fetus in the womb, and continues until we die. Our genetics and both the nutrients we receive before we are born and those we get through our diet in our youth have a major influence on the strength and endurance of our skeletal system.
Each of the 206 bones in your body is constantly undergoing a process of breakdown and renewal, even if you have never suffered a broken bone in your life. Your entire skeleton is completely replaced approximately every 10 years. The construction of bone tissue begins when we are a fetus in the womb, and continues until we die. Our genetics and both the nutrients we receive before we are born and those we get through our diet in our youth have a major influence on the strength and endurance of our skeletal system. It almost seems like a silly question, but it’s worth answering nonetheless. Why? Because it’s too important not to—a great many people could avoid the potentially serious health problems associated with being overweight or obese by losing the extra pounds. And the sooner the better.
It almost seems like a silly question, but it’s worth answering nonetheless. Why? Because it’s too important not to—a great many people could avoid the potentially serious health problems associated with being overweight or obese by losing the extra pounds. And the sooner the better.

