Summer Fun and Water Safety
 Summertime’s here and for many children around the country that means fun in the water!
Summertime’s here and for many children around the country that means fun in the water!
But here’s the catch… Whether it happens to be a neighborhood pool, a lake near a favorite camping spot or the ocean right across the beach from a vacation rental, playing in and around the water comes with certain risks. And while the rate of accidental death by drowning has been dropping over the years, it is still the leading cause of accidental deaths for children between the ages of one and four.
We believe that parents should pay special attention to these risks—especially at this time of the year. Here are some safety tips for parents whose kids will be spending time around the water during the next few months.
Tip #1. Teach your child to swim.
This is one of the best things you can do for your child, and the earlier the better. You can start familiarizing your child with water as an infant so they do not develop a fear of it. Ensuring that your child receives swimming lessons is especially important if he or she comes from a family of non-swimmers, as children from these households are eight times more likely to drown than children who come from swimming households. If your child can’t swim, be sure he or she wears a life jacket at all times around open water. Children should be taught never to swim alone and not to play around unattended pools or drains.
Tip #2. Remove drowning hazards.
Children—especially young ones—can drown not only in a pool, but also in a tub, toilet, or even a bucket with only a few inches of water at the bottom. Keep bathroom and laundry room doors shut and keep toilet seat lids closed. It’s also a good idea to install a child safety lock on the seat. Keep buckets drained of liquid and store them upside-down when they’re not in use. Remove water from the tub or any kind of wading pool immediately after use.
Tip #3. Be nearby at all times.
Always remain within arm’s reach of your young child in any setting where there is water, including pools, tubs, ponds and buckets. Never leave your child unattended in the tub, even for a minute. Two thirds of home deaths from drowning (apart from pools) occur in the bathtub!
Tip #4. Watch your child constantly.
Children playing in or near the water need to be supervised at all times, even if they know how to swim. It is important not to be distracted by talking on the phone, sending text messages or reading a book, as children can drown very quickly and quietly. Most deaths from drowning occurred just after an adult was watching them. If you find your child is missing, check the water first.
Tip #5. Put up safety barriers.
If you have a pool or spa at home, be sure it is surrounded on all sides by a fence that is at least four feet high. The fence should have a gate that locks automatically, and alarms to both the gate and pool area should be installed. Remember to cover and lock the pool or spa when you are not using it.
Tip #6 Learn CPR.
Children who are rescued from drowning need to receive CPR as soon as possible to decrease the likelihood of death or brain damage. Don’t wait for the paramedics to arrive. Learn CPR and do something!

 With warm summer weather in the forecast, many people take the opportunity to spend more time in the great outdoors. Camping, hiking and boating are all on the agenda! But beware—being outside means sharing the wilderness with all of the creatures that live there. This includes the insects!
With warm summer weather in the forecast, many people take the opportunity to spend more time in the great outdoors. Camping, hiking and boating are all on the agenda! But beware—being outside means sharing the wilderness with all of the creatures that live there. This includes the insects!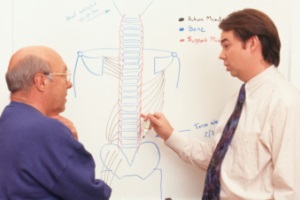 According to the National Institutes of Health and Dr. Michael S. Wilkes of the Western Journal of Medicine, “Despite a plethora of research intended to guide physicians in their management of back pain, physicians still hold strong non-evidence based beliefs dating back to the 19th century.” What beliefs is Dr. Wilkes referring to? He’s talking about the long-held conventional wisdom that says bed rest is one of the best ways to treat back pain.
According to the National Institutes of Health and Dr. Michael S. Wilkes of the Western Journal of Medicine, “Despite a plethora of research intended to guide physicians in their management of back pain, physicians still hold strong non-evidence based beliefs dating back to the 19th century.” What beliefs is Dr. Wilkes referring to? He’s talking about the long-held conventional wisdom that says bed rest is one of the best ways to treat back pain.
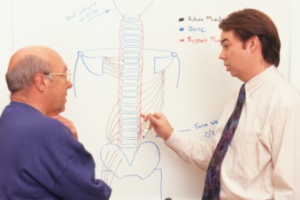 According to the National Institutes of Health and Dr. Michael S. Wilkes of the Western Journal of Medicine, “Despite a plethora of research intended to guide physicians in their management of back pain, physicians still hold strong non-evidence based beliefs dating back to the 19th century.” What beliefs is Dr. Wilkes referring to? He’s talking about the long-held conventional wisdom that says bed rest is one of the best ways to treat back pain.
According to the National Institutes of Health and Dr. Michael S. Wilkes of the Western Journal of Medicine, “Despite a plethora of research intended to guide physicians in their management of back pain, physicians still hold strong non-evidence based beliefs dating back to the 19th century.” What beliefs is Dr. Wilkes referring to? He’s talking about the long-held conventional wisdom that says bed rest is one of the best ways to treat back pain. Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) in winter is a widely-known phenomenon. There is less sunlight during winter days, which affects the serotonin (“happy” hormones) produced in response to light striking our pineal gland, causing depression and listlessness. But not many people are aware that SAD has a summer equivalent as well. Studies performed on people in countries near the equator have found that their populations often suffer from SAD in the summer months. But what can be its cause?
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) in winter is a widely-known phenomenon. There is less sunlight during winter days, which affects the serotonin (“happy” hormones) produced in response to light striking our pineal gland, causing depression and listlessness. But not many people are aware that SAD has a summer equivalent as well. Studies performed on people in countries near the equator have found that their populations often suffer from SAD in the summer months. But what can be its cause? With summer weather heating things up across much of the country, swimming is a great way to cool off and have some fun! But did you know that it’s also an excellent way to increase your fitness, help control your weight and improve your overall mood? Plus, swimming is a type of exercise that people of any age and physical ability can enjoy. It’s easy on the musculoskeletal system while at the same time providing a good aerobic workout.
With summer weather heating things up across much of the country, swimming is a great way to cool off and have some fun! But did you know that it’s also an excellent way to increase your fitness, help control your weight and improve your overall mood? Plus, swimming is a type of exercise that people of any age and physical ability can enjoy. It’s easy on the musculoskeletal system while at the same time providing a good aerobic workout.